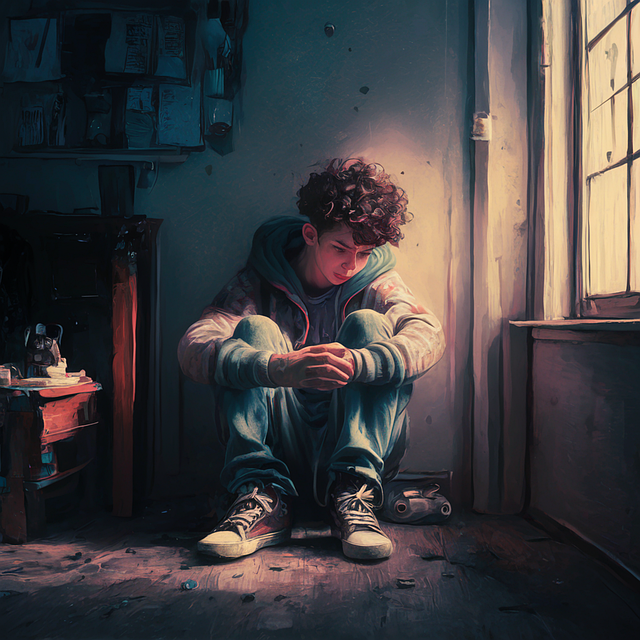
Depression in young children often shows as behavioral changes rather than verbal sadness. Early intervention is crucial, focusing on cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) to address negative thought patterns and build emotional regulation skills. Lifestyle changes, such as healthy diets, exercise, and sleep hygiene, alongside mental wellness coaching programs, foster resilience. Community outreach initiatives raise awareness, ensure access to therapy services, and create safe environments for emotional expression, ultimately preventing long-term depression in young individuals.
Depression among young children is a growing concern, yet preventative strategies often lack emphasis. This article delves into essential methods to foster mental well-being in children, focusing on early recognition of depressive signs. We explore the power of supportive systems and evidence-based therapies tailored for children’s unique needs. Additionally, we discuss lifestyle changes, resilience-building techniques, and coping skills to create a robust prevention framework. By implementing these strategies, parents, caregivers, and educators can effectively navigate and mitigate childhood depression, ensuring a brighter future for our young minds.
- Recognizing the Signs of Depression in Young Children
- The Role of Early Intervention and Support Systems
- Evidence-Based Therapies for Children's Mental Health
- Incorporating Lifestyle Changes for Improved Well-being
- Building Resilience and Coping Skills for Long-Term Prevention
Recognizing the Signs of Depression in Young Children

Depression isn’t exclusively an adult concern; young children can also experience this complex emotion. Recognizing the signs early is crucial for effective therapy and support. While younger kids might not verbalize their feelings as adults do, they may exhibit changes in behavior and mood that signal a need for help. Symptoms to look out for include persistent sadness, irritability, loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, difficulty concentrating, and even talk of death or suicide. These signs can be subtle and vary from child to child, so attentive caregivers are key.
If you suspect a young child is dealing with depression, consider the role of mental health policy analysis and advocacy in your community. Initiatives like Community Outreach Program Implementation can raise awareness about mental health issues in children and ensure access to appropriate therapy services. By embracing mind over matter principles, we can foster an environment where children feel comfortable expressing their emotions, seek help when needed, and develop resilience to overcome depression.
The Role of Early Intervention and Support Systems

Early intervention plays a pivotal role in depression prevention, especially for young children. Recognizing and addressing depressive symptoms at an early stage can significantly alter the trajectory of mental health issues later in life. Therapies tailored for young minds, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), have proven effective in treating childhood depression. These therapies empower children to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors, fostering resilience against future setbacks.
Strong support systems are equally crucial. Family and peers can play a vital role in reducing the stigma surrounding mental illness and encouraging open conversations about emotional well-being. Incorporating practices like mindfulness meditation into daily routines can also be beneficial. Mindfulness helps children develop self-awareness, emotional regulation skills, and stress resilience, all of which contribute to burnout prevention and overall mental health maintenance.
Evidence-Based Therapies for Children's Mental Health

Evidence-based therapies have proven effective in treating depression among young children, offering a promising path for prevention. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), for instance, focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to depressive symptoms. This approach empowers children to develop healthier coping mechanisms and enhance their problem-solving skills. Another powerful tool is Interpersonal Psychotherapy (IPT), which addresses the impact of social relationships on mental health. IPT helps young individuals navigate difficulties in communicating with peers or family members, fostering better connections and reducing social isolation—key factors in depression prevention.
Integrating these evidence-based practices into mental health policy analysis and advocacy is essential. By promoting access to quality therapy for young children, communities can foster inner strength development early on. This proactive approach not only supports individual well-being but also contributes to a more resilient and healthy society.
Incorporating Lifestyle Changes for Improved Well-being

Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly impact depression prevention and overall well-being, especially for young children who may be experiencing their first episode. Simple yet effective strategies include fostering healthy eating habits by focusing on nutrient-rich foods that support brain health. Regular physical activity is another powerful tool; even short bursts of exercise have been shown to boost mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Additionally, promoting good sleep hygiene ensures adequate rest, which is crucial for emotional regulation.
Self-awareness exercises and practicing mindfulness can also be beneficial. Encouraging children to engage in activities that foster self-esteem improvement, such as journaling or creative expression, can help them process emotions and build resilience. Burnout prevention techniques, like setting boundaries and learning to say no, are essential to maintaining a healthy work-life balance, which is particularly relevant as therapy for young children depression often involves intense treatment plans.
Building Resilience and Coping Skills for Long-Term Prevention

Building resilience and coping skills from a young age is a powerful strategy for long-term depression prevention. Therapy for young children can play a pivotal role in fostering mental wellness by teaching them healthy ways to navigate emotions, manage stress, and cope with life’s challenges. Mental wellness coaching programs designed specifically for children often incorporate play therapy, art therapy, and cognitive behavioral techniques to help them develop essential coping skills. These skills empower kids to understand their feelings, express them constructively, and build a positive mindset, all of which are crucial in preventing depressive episodes later in life.
Coping skill development goes beyond individual therapy; it can also be enhanced through family involvement and community support systems. Encouraging open conversations about mental health at home, fostering a safe environment for expression, and teaching positive thinking techniques as part of daily routines contribute to building resilience. By equipping young individuals with these tools, they gain the confidence to handle difficult situations, bounce back from setbacks, and maintain their mental wellness over time, effectively preventing depression.
Depression among young children is a growing concern, but with the right strategies, it can be prevented. By recognizing early signs, implementing evidence-based therapies, and adopting lifestyle changes, parents and caregivers can create robust support systems. Incorporating resilience-building activities equips children with essential coping skills, fostering long-term mental well-being. Early intervention is key to preventing depression in young individuals, ensuring they grow up with the tools needed to navigate life’s challenges.