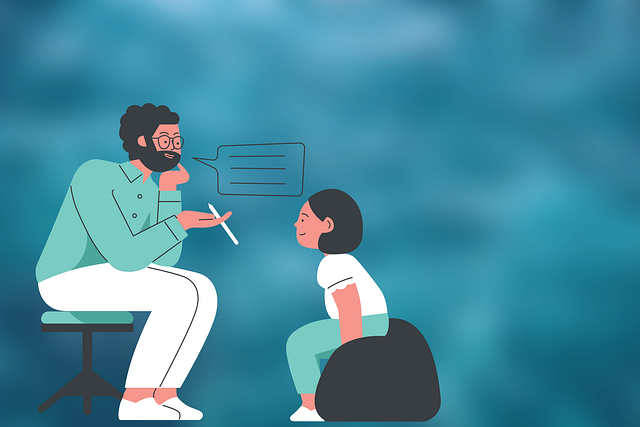
Dissociative Disorder (DD), marked by identity, memory, and reality disruptions, requires specialized therapy. Mental health professionals employ structured interviews, compassion cultivation practices, and tailored strategies to address DD's complex nature. Key approaches include cognitive behavioral therapy for trauma processing, self-care for therapist burnout prevention, and social skills training. Safe practices, regular risk assessments, and evidence-based techniques ensure effective treatment, focusing on symptom management and underlying cause resolution, particularly in Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) cases. Continuous evaluation and client feedback integration refine therapy strategies over time, catering to DD patients' evolving needs.
Mental health professionals play a vital role in treating dissociative disorder, a complex condition with unique challenges. This article delves into the intricacies of managing this disorder, focusing on comprehensive risk assessment strategies essential for safe and effective therapy. We explore symptoms, diagnosis, and the specific risks associated with treatment. By understanding these risks, professionals can implement safe practices, adapt strategies over time, and ensure optimal care for clients navigating dissociative disorder, enhancing outcomes in therapy.
- Understanding Dissociative Disorder: Symptoms and Diagnostik
- The Role of Mental Health Professionals in Therapy
- Identifying Risks Specific to Dissociative Disorder Treatment
- Implementing Safe Practices for Effective Therapy
- Continuous Risk Assessment: Adapting Strategies Over Time
Understanding Dissociative Disorder: Symptoms and Diagnostik

Dissociative Disorder (DD) is a complex mental health condition characterized by disruptions in an individual’s sense of identity, memory, and perception of reality. It involves a disconnection from one’s thoughts, feelings, and surroundings, often leading to symptoms that can be challenging to recognize and diagnose. Professionals in the mental health field must be adept at identifying DD as it can manifest in various forms, including Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID), where individuals experience multiple distinct personalities or states.
The diagnostic process for DD involves a thorough evaluation by qualified therapists who employ structured clinical interviews and standardized assessment tools. Symptoms may include depersonalization, where people feel detached from themselves, and derealization, characterized by feelings of unreality in the environment. To offer effective therapy for Dissociative Disorder, mental health professionals should incorporate compassion cultivation practices, emphasizing self-care and resilience building. These approaches can help individuals with DD develop coping mechanisms to manage symptoms and enhance their overall well-being.
The Role of Mental Health Professionals in Therapy

Mental health professionals play a pivotal role in guiding individuals towards healing and recovery. They offer therapy sessions, providing safe spaces for clients to explore their emotions, memories, and experiences, especially those with complex conditions such as dissociative disorders. These professionals employ various techniques, including empathy building strategies, to foster trust and understanding, which are essential for effective treatment.
Through skilled interaction and risk management planning, they create an environment that encourages open communication. By implementing confidence-boosting measures, therapists empower their clients to confront challenges, process traumatic events, and integrate fragmented memories—a critical aspect of therapy for dissociative disorders. This holistic approach ensures individuals receive the support needed to navigate their mental health journeys with resilience and hope.
Identifying Risks Specific to Dissociative Disorder Treatment

Mental health professionals treating patients with Dissociative Disorder (DD) face unique challenges due to the complex nature of the condition. When providing therapy for dissociative disorder, identifying specific risks and implementing tailored strategies is paramount. One significant risk lies in the potential for re-traumatization during therapy, as DD often involves profound dissociation from traumatic memories. Therefore, therapists must create a safe and supportive environment, utilizing techniques like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to help patients process and integrate traumatic experiences gradually.
Furthermore, self-care practices are essential for professionals treating DD. Given the emotional intensity of this disorder, therapists may experience high levels of stress and burnout. Encouraging positive thinking and healthy coping mechanisms can mitigate these risks. Social skills training is another valuable tool; it equips both professionals and patients with the ability to navigate interpersonal relationships effectively, enhancing overall treatment outcomes.
Implementing Safe Practices for Effective Therapy

Implementing safe practices is paramount for mental health professionals to ensure effective therapy and mitigate risks associated with complex conditions like dissociative disorders. These disorders, characterized by a disconnection from reality and memory lapses, demand a nuanced approach. Therapists must create a structured environment where clients feel secure to explore their traumas and experiences. This involves establishing clear boundaries, ensuring confidentiality, and utilizing evidence-based techniques tailored for dissociation.
Regular training in stress management workshops and emotional regulation strategies is essential. Mental wellness podcast series production can also serve as valuable resources, offering insights into the latest research and practical tips. By integrating these educational tools, professionals enhance their ability to support clients effectively while managing potential risks inherent in treating dissociative disorders.
Continuous Risk Assessment: Adapting Strategies Over Time

In the dynamic field of mental health care, continuous risk assessment is an evolving practice that requires professionals to adapt their strategies over time. This nuanced approach recognizes that client needs and presentation of conditions like dissociative disorders can change, necessitating flexible interventions. Regular and thorough evaluations allow therapists to track progress, identify emerging risks, and tailor treatment plans accordingly. By integrating feedback from clients, observations, and research findings, mental health professionals can refine their strategies within the therapy for dissociative disorder framework.
This adaptive approach fosters a more holistic understanding of client experiences and promotes effective coping skills development. As new insights emerge through ongoing assessment, mental wellness podcast series production or the integration of innovative coaching programs (like those focused on mental wellness) can be incorporated into treatment plans. This ensures that professionals remain at the forefront of evidence-based practices, enabling them to provide the most comprehensive support for their clients’ evolving needs.
Mental health professionals play a crucial role in providing therapy for dissociative disorder, but they must also navigate distinct risks associated with this complex condition. By understanding the symptoms and implementing safe practices, professionals can offer effective treatment while ensuring their own well-being. Continuous risk assessment is essential to adapt strategies over time, fostering a supportive and secure environment for both clients and therapists. This comprehensive approach to therapy for dissociative disorder enhances outcomes and promotes resilience for all involved.