Depression in elderly individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires a nuanced approach due to age-related changes and unique ASD traits. Tailored therapy, including Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), focuses on self-esteem improvement and conflict resolution techniques for enhanced resilience. Mental health education programs specifically designed for this demographic increase awareness of depressive symptoms and encourage help-seeking behaviors. Early identification through targeted screenings is crucial for timely intervention. Therapy for Elders Autism Spectrum Disorder combines CBT, mindfulness meditation, lifestyle modifications, crisis intervention, support groups, art/music therapy, and building supportive networks to prevent depression and improve quality of life.
Depression prevention strategies are essential for improving the mental well-being of elderly individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This comprehensive guide explores various therapeutic approaches tailored to the ASD population, from recognizing depressive symptoms in the elderly with ASD to lifestyle modifications and building robust support systems. By integrating family, community, and professional networks, we can enhance the effectiveness of therapy for elders with autism spectrum disorder, fostering a more inclusive and supportive environment.
- Recognizing Depression in Elderly Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Therapeutic Approaches for Managing and Preventing Depression in ASD Population
- Lifestyle Modifications to Enhance Mental Well-being for Elders with ASD
- Building Support Systems: Family, Community, and Professional Networks
Recognizing Depression in Elderly Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)

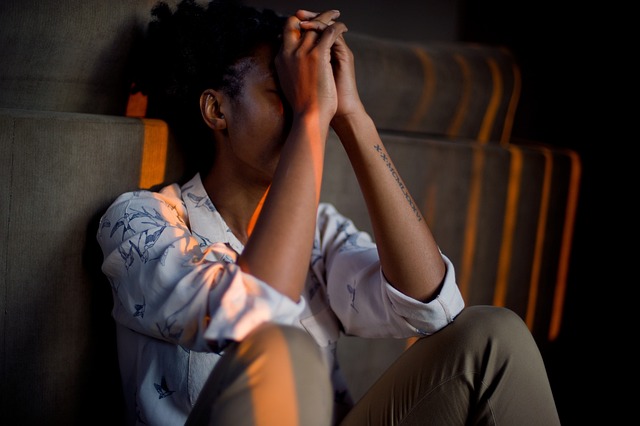
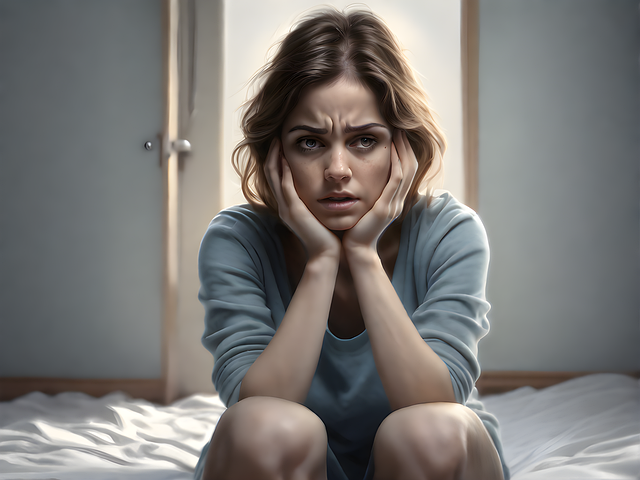
Depression among elderly individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can present unique challenges due to both age-related changes and the distinct characteristics of ASD. Recognizing depression in this population requires a nuanced approach. Often, symptoms may manifest differently than in neurotypical individuals. For example, low mood or social withdrawal could be attributed to the individual’s natural preferences or challenges with communication rather than depressive disorder. Thus, careful assessment is crucial to differentiate between ASD traits and potential signs of depression.
Therapy for elders with autism spectrum disorder plays a pivotal role in prevention strategies. Tailored interventions focusing on self-esteem improvement and conflict resolution techniques can enhance resilience and coping mechanisms. Mental health education programs designed specifically for this demographic can increase awareness about depressive symptoms, encourage help-seeking behaviors, and foster supportive environments. Early identification through targeted screenings and continued monitoring is vital to ensure timely intervention and improved quality of life.
Therapeutic Approaches for Managing and Preventing Depression in ASD Population

The management and prevention of depression in individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often require tailored therapeutic approaches that address their unique challenges. One effective strategy is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to depressive symptoms. CBT for ASD may include social skills training, teaching emotion recognition, and developing coping strategies.
Additionally, mindfulness meditation has gained prominence as a valuable tool for emotional healing processes in this population. By focusing on the present moment and cultivating awareness, individuals with ASD can learn to regulate their emotions, enhance focus, and build resilience against depressive episodes. Confidence-boosting techniques, such as positive reinforcement and exposure therapy, also play a significant role in empowering individuals with ASD to navigate social interactions and challenges more effectively, thereby reducing the risk of depression.
Lifestyle Modifications to Enhance Mental Well-being for Elders with ASD

Many elders with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face unique challenges when it comes to mental health. However, lifestyle modifications can significantly enhance their well-being and provide effective tools for depression prevention. Establishing a structured daily routine, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep, forms the foundation of these strategies. Encouraging social interactions tailored to individual preferences can foster a sense of belonging, combat loneliness, and improve mood. Additionally, engaging in relaxing activities like mindfulness practices or creative outlets can serve as powerful stress management techniques, promoting inner strength development.
Therapy for Elders with ASD should incorporate crisis intervention guidance tailored to their specific needs. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has proven effective, teaching individuals how to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. Support groups offer a safe space for sharing experiences and building community, while art or music therapy can provide nonverbal avenues for expression and emotional release. By integrating these lifestyle modifications and therapeutic interventions, elders with ASD can better navigate mental health challenges and cultivate resilience.
Building Support Systems: Family, Community, and Professional Networks

Building strong support systems is a vital aspect of depression prevention and managing mental health, especially for individuals navigating complex conditions like autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in later life. Family and community connections can provide a sense of belonging and understanding, offering non-judgmental spaces to share experiences and seek comfort. For elders with ASD, these networks can be particularly crucial, as they may face unique challenges in social interaction and communication. Encouraging participation in community groups or clubs aligned with their interests can foster new friendships and create opportunities for regular social engagement.
Professional networks, including therapists and mental wellness coaches, play a significant role in supporting individuals’ mental health journeys. Therapy tailored to the specific needs of elders with ASD can help them develop coping strategies and enhance their overall well-being. Mental wellness coaching programs designed for this demographic may include self-care routine development, stress management workshops, and personalized guidance. These professional interventions, combined with strong community support, create a comprehensive strategy to prevent depression and promote mental resilience.
Depression prevention in elderly individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires a multi-faceted approach. By recognizing early signs through tailored assessments, implementing therapeutic strategies such as cognitive behavior therapy, and adopting lifestyle modifications like regular exercise and structured routines, we can significantly enhance mental well-being. Building robust support systems that involve family, community, and professional networks is vital for providing ongoing assistance and fostering resilience against depression in this unique population. In terms of therapy for elders with autism spectrum disorder, a combination of targeted interventions and holistic care strategies proves most effective in preventing and managing depressive symptoms.