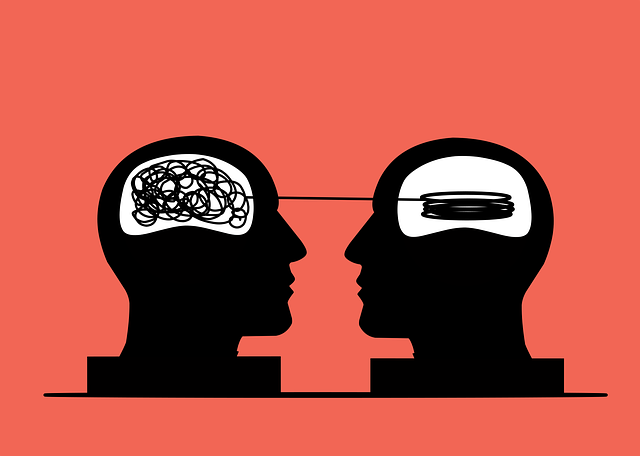
The text discusses how mental health stigma hinders access to support, leading to the development of programs like Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy (WREST) focused on destigmatization. REST incorporates culturally sensitive practices like conflict resolution and coping skills training to foster open dialogue, reduce anxiety, and improve therapy accessibility. An ideal mental health education program is diverse, holistic, and includes evidence-based therapies like CBT and mindfulness. By combining individual and group sessions, REST empowers individuals to heal emotionally, boost self-esteem, and enhance overall well-being. Program effectiveness is measured through surveys, feedback, and tracking empathy-building strategies adopted by participants.
“Mental health education programs play a pivotal role in fostering well-being and reducing stigma. This article delves into the strategic design of such initiatives, emphasizing the intricate balance between understanding societal stigma and its impact on program structure. We explore key components that constitute an effective mental health education program, highlighting the integration of evidence-based therapies for optimal outcomes. Furthermore, we present a case study of the Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy Model, offering insights into its implementation and evaluation.”
- Understanding Mental Health Stigma and Its Impact on Program Design
- Key Components of an Effective Mental Health Education Program
- Incorporating Evidence-Based Therapies for Optimal Results
- Implementing and Evaluating the Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy Model
Understanding Mental Health Stigma and Its Impact on Program Design

Mental health stigma, a pervasive issue, significantly influences program design for initiatives like Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy. Stigma often leads to misconceptions and fear surrounding mental illness, creating barriers for individuals seeking support. Understanding its impact is crucial in crafting effective therapy programs. Many individuals delay or avoid treatment due to the negative perceptions associated with mental health struggles, which can exacerbate existing issues.
Addressing stigma through education and awareness is a key aspect of cultural sensitivity in mental healthcare practice. By incorporating techniques like conflict resolution and promoting coping skills development, programs can foster an inclusive environment. This approach encourages open dialogue, reduces anxiety, and facilitates access to much-needed therapy. Such strategies ensure that program design not only addresses the symptoms but also breaks down societal barriers, ultimately enhancing the therapeutic experience for all participants.
Key Components of an Effective Mental Health Education Program

An effective mental health education program should be multifaceted and inclusive, incorporating various elements to ensure comprehensive learning. Firstly, it must provide accurate and up-to-date information about mental health conditions, symptoms, and available treatments, fostering a culture of open dialogue and reducing stigma. This includes teaching students about different therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and mindfulness meditation, empowering them to make informed decisions regarding their well-being.
Additionally, these programs should focus on self-care practices tailored to individual needs. This could involve encouraging regular exercise, healthy eating, and sufficient sleep as foundational pillars of mental health. Moreover, risk management planning is crucial for mental health professionals; the curriculum should equip students with strategies to handle stress, prevent burnout, and maintain their own psychological resilience, mirroring the practices offered by Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy.
Incorporating Evidence-Based Therapies for Optimal Results

Incorporating evidence-based therapies is paramount when designing a mental health education program aimed at achieving optimal results. One such effective approach is Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy, which has proven successful in enhancing self-care routine development for better mental health. This therapy focuses on empowering individuals to cultivate a positive sense of self, fostering emotional healing processes and facilitating self-esteem improvement.
By integrating these evidence-based strategies, the program can create a supportive environment that encourages participants to explore their emotions, build resilience, and adopt healthy coping mechanisms. Emphasizing both individual and group therapy sessions allows for a comprehensive understanding of emotional healing, enabling individuals to navigate life’s challenges with enhanced self-esteem and improved mental well-being.
Implementing and Evaluating the Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy Model

Implementing the Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy Model involves a structured approach to enhancing self-worth and confidence. This therapeutic program is designed to help individuals overcome emotional challenges, particularly those related to anxiety relief and building empathy within their communities. The model encourages active participation through various activities and discussions that foster emotional healing processes. By combining evidence-based techniques with group interactions, it aims to create a supportive environment where participants can learn and grow.
Evaluating this therapy’s effectiveness requires a comprehensive approach. Measuring self-esteem improvements can be achieved through pre-post surveys and qualitative feedback, assessing the impact on daily functioning and overall well-being. Additionally, tracking the adoption of empathy-building strategies among participants and their perceived benefits in managing interpersonal relationships adds depth to the evaluation. Such an assessment ensures that the program’s design and implementation align with its intended goals, fostering a more robust understanding of emotional healing and self-improvement processes.
Mental health education programs, like the Wheat Ridge Self-Esteem Therapy model presented here, are powerful tools for fostering well-being. By addressing stigma, incorporating evidence-based practices, and focusing on key components outlined in this article, we can create inclusive environments that empower individuals to take charge of their mental health. The successful implementation of such programs requires ongoing evaluation and adaptation, ensuring they remain effective and relevant in meeting the evolving needs of participants.